
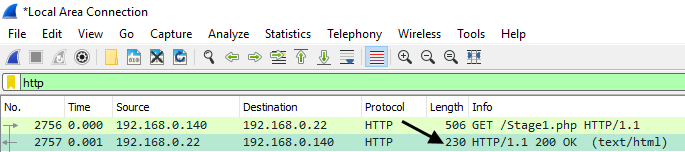
The single HTTP response message is thus broken into several pieces by TCP, with each piece being contained within a separate TCP segment (see Figure 1.24 in the text). In our case here, the HTML file is rather long, and at 4500 bytes is too large to fit in one TCP packet. In the case of our HTTP GET, the entity body in the response is the entire requested HTML file. Recall from Section 2.2 (see Figure 2.9 in the text) that the HTTP response message consists of a status line, followed by header lines, followed by a blank line, followed by the entity body. This multiple-packet response deserves a bit of explanation. Receive notifications of new posts by email.My homework is asking this question: Are there any HTTP status lines in the transmitted data associated with a TCP- induced “Continuation”? The text previous to the question states: In the packet-listing window, you should see your HTTP GET message, followed by a multiple-packet response to your HTTP GET request.

NetFlow (v9) v6 [Wireshark display filter:.IKEv1 v6/v4 (aggressive mode, main mode) [Wireshark display filter:.DNS v4/v6 (tons of RRs, UDP, TCP, fragmentation, DNSSEC validation, SERVFAIL, NXDOMAIN, ENDS(0) client subnet, EDNS(0) cookie, mDNS, dynamic update, zone change notification, IXFR, AXFR, TSIG).DHCPv6 ( stateful, stateless, prefix delegation).Referenced by the classical transport protocol port number. OSPFv3 for IPv6 (plain & authentication via IPsec authentication header AH).ICMPv4 (ping, timestamp, destination unreachable, time-to-live exceeded).ICMPv6 (RS, RA w/ RDNSS and DNSSL, NS, NA, DAD, MLD with hop-by-hop extension header (number 0), ping, destination unreachables, packet too big, time exceeded).ESP v6/v4 (IPv6 extension header number 50).AH v6 (IPv6 extension header number 51, used by OSPFv3).
Referenced by the IP Protocol Number, which is the “Next Header” field in IPv6 respectively the “Protocol” field in IP.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
